Medicinal uses, effects and benefits of horse mint
03/25/2018 / By Michelle Simmons

A review of studies published in the Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine discussed the medicinal and phytochemical properties of horse mint. The study review was conducted by a team of researchers from Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences and Tehran University of Medical Sciences in Iran. The research team reviewed studies that looked at the pharmacological activities, therapeutic indications, and phytochemicals of horse mint.
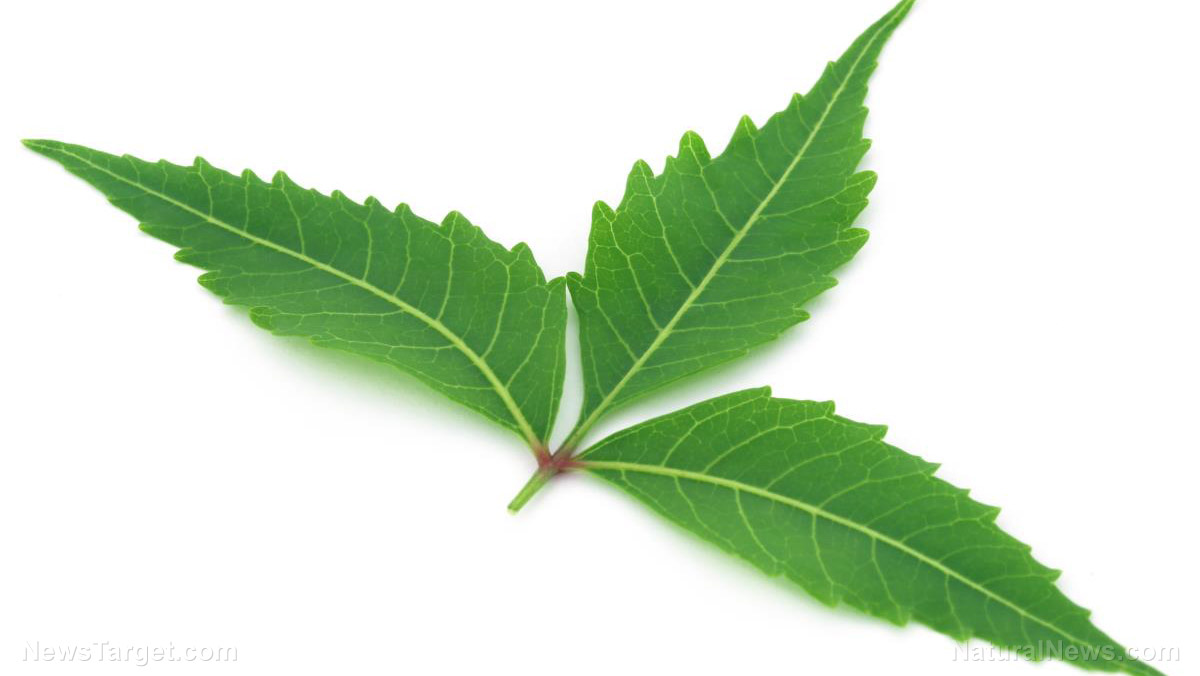
Also known as wild mint, horse mint (Mentha longifolia L.) is an herbal plant that contains various medicinal properties. It is native in Southeast Asia, but can also be found in Iran, where it is commonly consumed as a green vegetable and spice, or used as an additive with different foods. Moreover, the herb has been traditionally used for its therapeutic effects on different diseases, such as gastrointestinal disorders, respiratory problems, infectious diseases, inflammatory diseases, and menstrual problems. In addition, evidences also proved that the plant provides therapeutic benefits in different diseases, such as irritable bowel syndrome, amenorrhea, and oligomenorrhea, as well as in oxidative stress-associated diseases.
The review authors found that the different pharmacological activities of horse mint, such as antiparasitic, antimicrobial, anti-insect, antimutagenic, antinociceptive, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, keratoprotective, hepatoprotective, anti-diarrhea, and spasmolytic effects, were confirmed in earlier studies. Studies also indicated that the pharmacological action of horse mint can be attributed to its natural components, such as flavonoids, phenolic acids, cinnamates, ceramides, sesquiterpenes, terpenes, and terpenoids. These can potentially be used as novel medicinal sources for developing new drugs.
Nevertheless, the review authors suggested that further preclinincal and clinical investigations exploring therapeutic efficacy and safety of the herb and its phytoconstituents are needed. They also concluded that their findings confirm that horse mint has a great variety of therapeutic functions and various highly bioactive components.
“Further investigations to explore therapeutic efficacy, tolerability, and pharmaceutical properties of M. longifolia phytochemical agents are recommended,” they wrote.
More on the herbal plant horse mint
Horse mint is an herbal plant that belongs to the large mint family known as Lamiaceae, which has about 250 genera and 6,700 species, which include many popular herbs and garden plants such as lavender, sage, basil, rosemary, and mint. (Related: Ancient herbal mint remedy is effective, safe pain reliever, new study finds) It is a fast-growing, perennial herb that has creeps along an underground rootstock. In favorable conditions, it can grow up to 1.5 meters (m) high, but is typically between 0.5 to one meter high and even shorter in dry conditions. It has soft, long, and narrow with a sharp point leaves that are usually coarsely hairy as well as sparsely-toothed edges. The plant also has flowers, which vary in color from white to mauve, that are grouped into spikes at the tip of the stems. Its flowers are typically seen throughout November to April.
The herbal plant has a strong mint smell and taste that has been used not only in the kitchen, but also as a medicine. It is used in salads and vegetable dishes in the kitchen. Moreover, when in flower, horse mint attracts bees and butterflies. In addition,it can keep mosquitoes away when it is rubbed onto the body and bedding because of its strong smell.
Visit Herbs.news for more news coverage of medicinal herbs.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: herb, Herbal, herbal medicine, Herbs, horse mind, horse mint, Mentha longifolia, natural medicine, pharmacological activity, phytochemicals, phytoconstituents, plant, review, wild mint